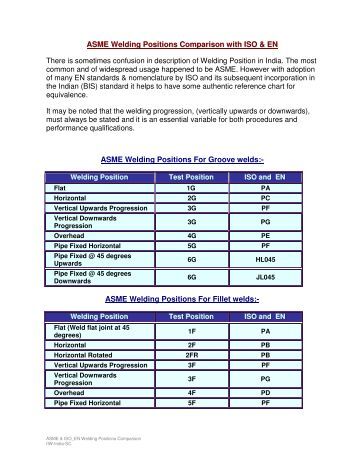
Asme Ix Welding Positions
What is ASME Section IX: ASME Section IX Code is set of rules, guidelines, and requirements for Welding, Brazing, and Fusing Qualifications. It is a reference code that helps for BPVC Construction Codes for Qualifications of Welder or Welding Operator, Brazer or Brazing Operator, and Fuser or Fusing Operator. Subsections of ASME Section IX. ASME IX covers the qualification of welders and welding operators, welding procedures, brazing operatives and brazing procedures for the complete range of ferrous and non-ferrous engineering. Oct 23, 2009 Position: Special Requirements: Diameters: All Diameters and product forms approved Ref QW211. Joint Type: All Joint Types Approved, a double sided weld will approve single sided. Fillet Welds: All weld sizes and parent metal thickness approved QW451.3 Note Fillet welds must be approved by a groove weld for pressure retention.
Welding Positions are the positional relation between the welder and the production piece to be welded. In ISO 15614-1, ASME IX and AWS D1.1 (referring to AWS A3.0), the ideals are pretty similar, but have a different naming system.
If you’d like to read some more on other issues, you can use our blog, or follow us on facebook, twitter and linkedin,
Below this is a diagram which you can use to define the horizontal positions (this means the weld progression is done horizontally). This whole article and the diagrams below will already be featuring the conversion between ISO standards to AWS / ASME standards naming system.
You’ll notice that you’ll essentially only need to pay attention to half of this diagram, as the other half is exactly the same (mirrored), which means the PC / 2G position is the same on either side of the plate or pipe.
Horizontal travel positions
PA / 1G / 1F: This is the flat position, in which the welder has the piece right below the torch, this is used for butt or groove welds, although it can be used for fillet welds.
PB / 2F: This is the horizontal position for fillet welds. The welder will be holding the torch at around 45º most of the times (although it depends on the plate or pipe position) with the piece right next to him:
PC / 2G: Commonly referred to as the horizontal position for butt welds. The piece will be directly parallel to the welders body and he’ll usually weld the piece while it is right in front of him:
PD / 4F: This is the overhead position for fillet welds. The welder will be holding the torch at around 45º most of the times (even if it depends on the plate or pipe position), this time while being below the piece.
PE / 4G: Overhead position for butt welds. The welder will be holding the torch from directly below the piece. It is quite hard as a position and requires proper weld parameter settings.
Uphill and Downhill travel positions
Okay so the previous part of this post with the respective diagram is essentially referring to the horizontal travel welding positions, in which the weld progression is perpendicular to the welder’s position. We shall now discuss the positions in which weld progression is parallel to the welder’s position.
PF / 3G Uphill: Vertical up for butt or fillet welds. The welder uses the metal from the lower parts of the test piece and some superficial tension to perform welding against the force of gravity, while aiming the torch at around 45º.
PG / 3G Downhill: Vertical down for butt or fillet welds. The welder will use the metal from the upper parts of the test piece and the electric arc’s own kinetic force (as well as some superficial tension) to maintain the weld puddle. This is a good position in terms of productivity, and there are already very competent systems to weld in this position on semi-automatic welding.
PH / 5G Uphill: Vertical up position for pipe butt welds. This is a very common way of welding pipes manually. The welder will be welding in three different positions, starting with the overhead position, then going through the horizontal position, and finishing on the flat position

PH / 5G Downhill: Vertical down position for pipe butt welds. This is a very productive way of welding pipes manually, but should be done only with specific equipment for pipe welding against the force of gravity. The welder will be welding in three different positions, starting with the flat position, then going through the horizontal position, and finishing on the overhead position.
H-L045 / 6G Uphill and J-L045 / 6G Downhill: The hardest positions for a welder to perform. Usually only performed on weld tests, in order to qualify a welder for all other positions. This is essentially the same as PH / PJ / 5G but with the pipe at a 45º angle.
J-L045 / 6G Downhill
Asme Ix Welding Positions Apprenticeship
So, to summarize, these are the comparisons between ISO standard positions and ASME / AWS nomenclature:
Welding Position (ISO) | Welding Position (ASME / AWS) |
| PA | 1G / 1F |
PB | 2F |
PC | 2G |
| PD | 4F |
PE | 4G |
PF | 3G Uphill |
PG | 3G Downhill |
PH | 5G Uphill |
PJ | 5G Downhill |
H-L045 | 6G Uphill |
| J-L045 | 6G Downhill |
I hope this has been helpful, if you’d like to read more, you may follow us on facebook, twitter and linkedin.
Asme Welding Procedures 31 3
You may also check our other blog posts here.
Best regards,
Tiago Pereira
CEO at WeldNote, Welding Management Software
Your reasoning is flawed and your answer incorrect.

Another example of reading the QW-4xx variables out of context.
QW-405.2 typically applies to general process qualification (groove welds, etc.).
QW-405.4 apples to special process qualifications (Hard facing or corrosion resistant overlay).
Asme Section 9 Welding Certification
These two variables are never called out together.
Regarding the application of supplementary essential variable QW-405.2, I suggest you read Interpretation IX-81-24 reply to question 1 states :
Asme Ix Welding Procedure
Reply (1): When applying QW-405.2, any position not involving the vertical uphill progression will qualify for all positions, except those involving the vertical uphill progression. Any position involving the vertical uphill progression win qualify for all positions, including those involving the vertical uphill progression. For example, qualification on a test coupon in the 2G position will qualify 4G and 5G downhill, but not 3G uphill. Qualification on a test coupon in 3G uphill progression will qualify 4G, 6G uphill progression, and all other positions.
John A. Henning
Asme Ix Welding Procedure
Welding & Materials
Asme 9 Welding Code
--
To post to this group, send email to material...@googlegroups.com
To unsubscribe from this group, send email to material...@googlegroups.com
For more options, visit this group's bolg at http://materials-welding.blogspot.com/
http://www.linkedin.com/groups/MaterialsWelding-122787?home=&gid=122787&trk=anet_ug_hm
The views expressed/exchnaged in this group are members personel views and meant for educational purposes only, Users must take their own decisions w.r.t. applicable code/standard/contract documents.
---
You received this message because you are subscribed to the Google Groups 'Materials & Welding' group.
To unsubscribe from this group and stop receiving emails from it, send an email to material...@googlegroups.com.
For more options, visit https://groups.google.com/d/optout.
